Outline
npx nestia sdkCollection of typed fetch functions with DTO structures.
Configure nestia.config.ts file and run npx nestia sdk command.
Then, @nestia/sdk will analyze your NestJS backend server code, and generate SDK (Software Development Kit) library composed with. The newly generated SDK library would be composed with DTO and fetch functions with type definitions following your NestJS server.
With the SDK library composed with RPC (Remote Procedure Call) functions, you can easily develop e2e test program. Also, frontend developers can utilize the SDK library to interact with your NestJS backend server, much safely and conveniently.
If you can’t imagine how the SDK library works, then look at the gif image of below. Left side is the NestJS backend server program, and right side is the Frontend program interacting with your server. Isn’t it look like much more convenient and safer than before Swagger Documents case?
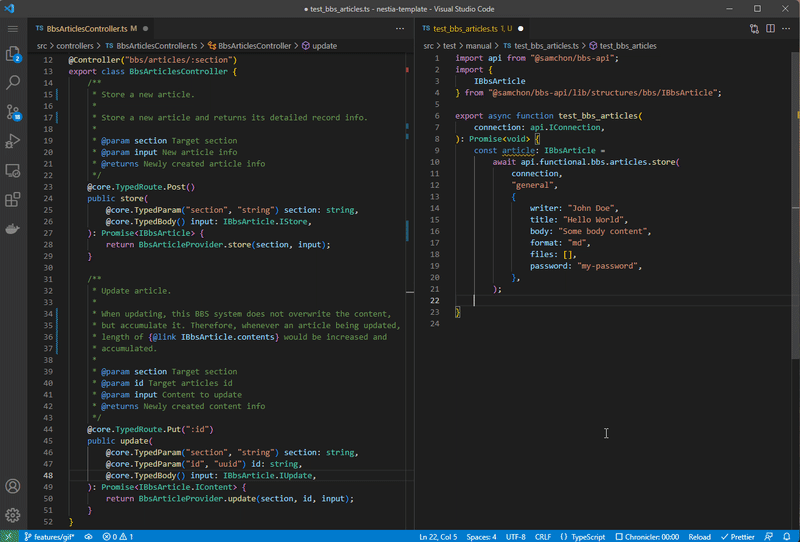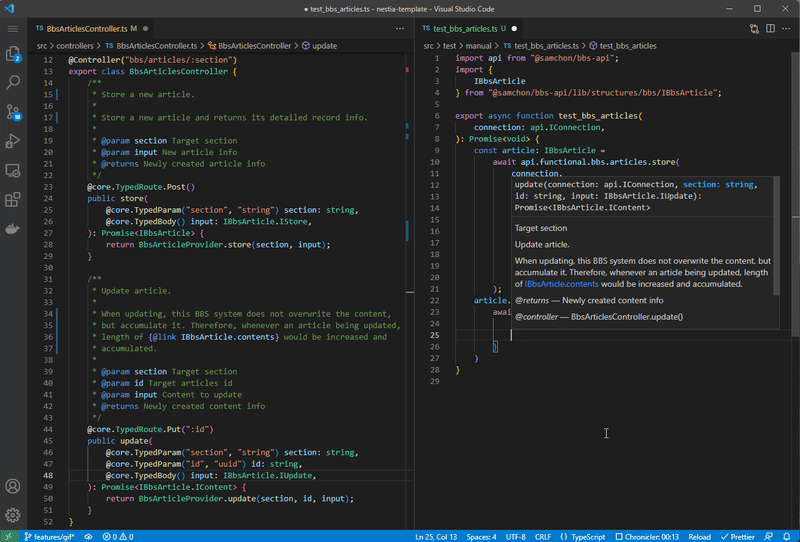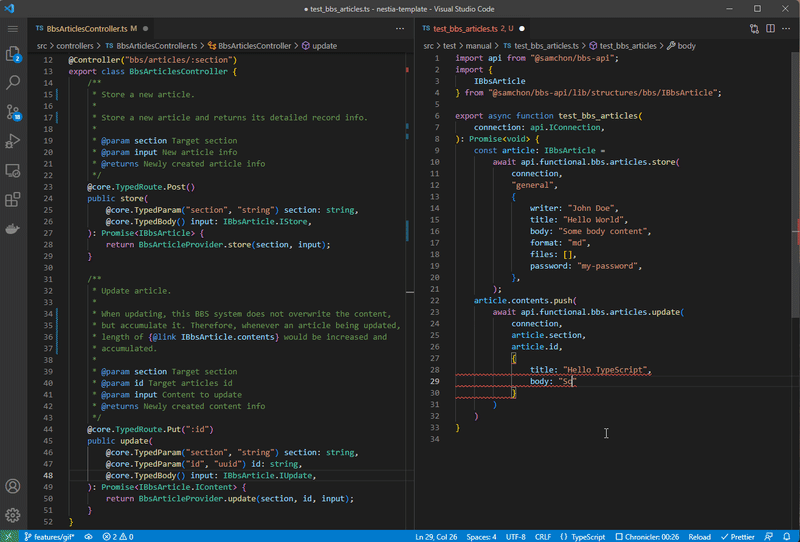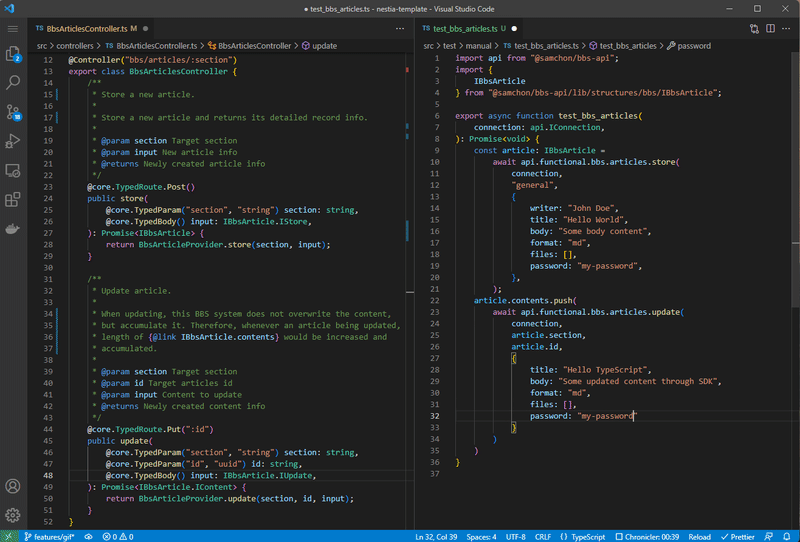
Left is NestJS server code, and right is client (frontend) code utilizing SDK
Application Module
import { INestiaConfig } from "@nestia/sdk";
import { NestFactory } from "@nestjs/core";
// import { FastifyAdapter } from "@nestjs/platform-fastify";
import { YourModule } from "./src/YourModule";
const NESTIA_CONFIG: INestiaConfig = {
input: async () => {
const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule);
// const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule, new FastifyAdapter());
// app.setGlobalPrefix("api");
// app.enableVersioning({
// type: VersioningType.URI,
// prefix: "v",
// })
return app;
},
output: "src/api",
distribute: "packages/api",
};
export default NESTIA_CONFIG;Make nestia.config.ts file and run npx nestia sdk command.
At first, create nestia.config.ts file through npx nestia init command. It would be placed on the top level directory of your NestJS backend project. For reference, tsconfig.json file also must be placed in the top level directory, too. After creation, configure the nestia.config.ts file referencing above example code and type definition.
At least, you’ve to configure those two properties:
input: Accessor of controller classesoutput: Path of output directory for SDK library
When you’ve completed above configuration, just run npx nestia sdk command. Then, SDK library would be newly generated, and placed into the $config.output directory following your nestia.config.ts configuration.
Clone Mode
import { INestiaConfig } from "@nestia/sdk";
import { NestFactory } from "@nestjs/core";
// import { FastifyAdapter } from "@nestjs/platform-fastify";
import { YourModule } from "./src/YourModule";
const NESTIA_CONFIG: INestiaConfig = {
input: async () => {
const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule);
// const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule, new FastifyAdapter());
// app.setGlobalPrefix("api");
// app.enableVersioning({
// type: VersioningType.URI,
// prefix: "v",
// })
return app;
},
output: "src/api",
clone: true,
distribute: "packages/api",
};
export default NESTIA_CONFIG;If you configure clone property to be true in the nestia.config.ts file, all of DTO structures used in the backend server would be cloned into the structures directory, and the SDK library would be refer to the cloned DTO structures instead of the original.
This clone mode is useful when you’d not separated DTO structures from the ORM models. When you’re using TypeORM or Prisma, and returning the ORM generated instance directly in the controller without independent DTO structure definition, your SDK library requires the TypeORM or Prisma dependency install. By the dependency, client (frontend) developers may install the ORM library that they never need.
In that case, it would better to remove the dependency by using this clone mode.
Propagation Mode
import { INestiaConfig } from "@nestia/sdk";
import { NestFactory } from "@nestjs/core";
// import { FastifyAdapter } from "@nestjs/platform-fastify";
import { YourModule } from "./src/YourModule";
const config: INestiaConfig = {
input: async () => {
const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule);
// const app = await NestFactory.create(YourModule, new FastifyAdapter());
// app.setGlobalPrefix("api");
// app.enableVersioning({
// type: VersioningType.URI,
// prefix: "v",
// })
return app;
},
output: "src/api",
propagate: true,
distribute: "packages/api",
};
export default config;Returns IPropagation typed instance instead of throwing exception.
When you configure propagate property of nestia.config.ts file, all of SDK functions generated by @nestia/sdk will perform propagation mode. The propagation mode means that never throwing exception (HttpError) even when response status code is not 200 (or 201), but just returning the IPropagation typed object, which can specify its body data type through discriminated union determined by status code.
Looking at below code tabs one by one, then you may understand exactly, what the propagation mode is. As you can see from below example code, @TypedException() decorator function can be utilized to define the failure type with specific status code. Also, if returned status code is out of pre-defined, the IPropagation.data type would be automatically casted to unknown type.
import core from "@nestia/core";
import { Controller } from "@nestjs/common";
import typia, { tags } from "typia";
import { IBbsArticle } from "@api/lib/structures/IBbsArticle";
@Controller("bbs/articles/:section")
export class BbsArticlesController {
/**
* Update an article.
*
* @param section Section code
* @param id Target article ID
* @param input Content to update
* @returns Updated content
*/
@core.TypedException<TypeGuardError.IProps>(400)
@core.TypedRoute.Put(":id")
public async update(
@core.TypedParam("section") section: string,
@core.TypedParam("id") id: string & tags.Format<"uuid">,
@core.TypedBody() input: IBbsArticle.IStore,
): Promise<IBbsArticle> {
return {
...typia.random<IBbsArticle>(),
id,
section,
...input,
};
}
}CLI Arguments
npx nestia sdk
npx nestia sdk --config nestia2.config.ts
npx nestia sdk --project tsconfig2.json
npx nestia sdk --config nestia3.config.ts --project tsconfig3.tsconfig.jsonIf you have a special configuration file that its file name is not nestia.config.ts or the configuration file is not placed on the root directory of the project, you can specify it with --config option like npx nestia sdk --config another.config.ts.
Also, if you have a special tsconfig.json file or the project file is not located in the root directory of the project, you can specify it with --project argument like npx nestia sdk --project another.tsconfig.json, too.